

Mathematics of growth generation time Growth equation # of generations Can recover viable culture even after a year of sitting on shelf!
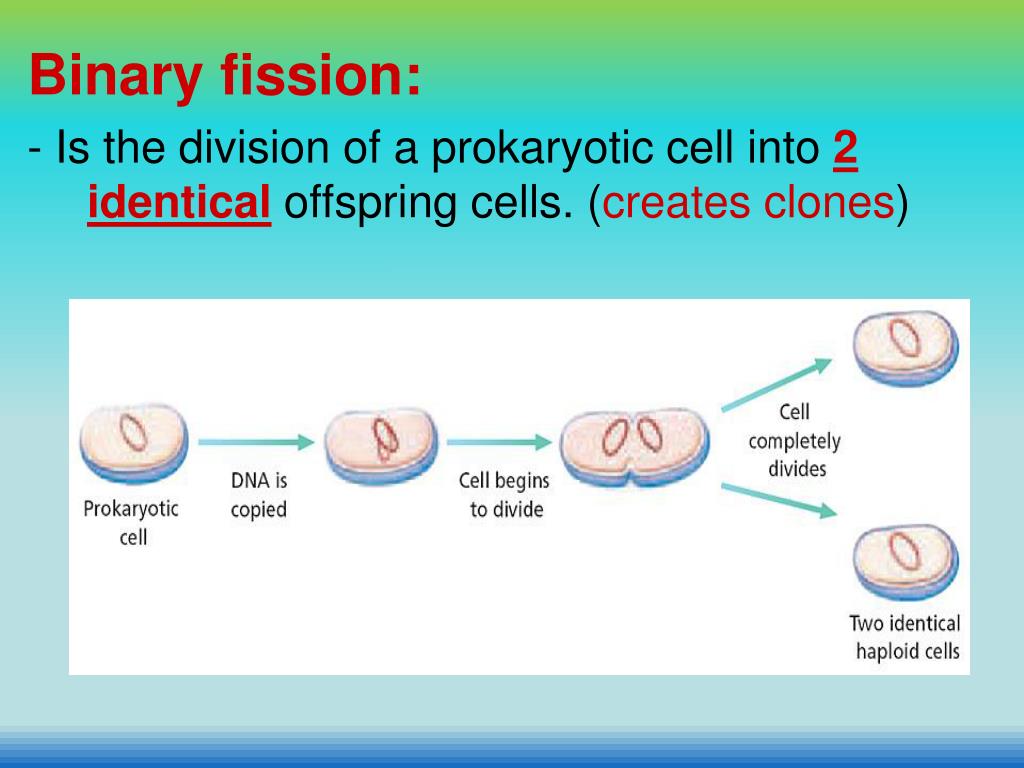
Still better, transfer to stab tube (soft nutrient agar), stopper and seal with airtight seal. Better, transfer to slants (tubes), store capped in refrigerator once grown. Don't store cultures at room temperature on plates (ready exposure to oxygen, dessication, high temperature speeds oxidation reactions). Note: in practice, try to prolong stationary phase, reduce death phase.Note that death is exponential 90% of cells die in certain time, another 90% in same time period, etc. Continued accumulation of wastes, exposure to oxygen, loss of cell's ability to detoxify toxins, etc.Can be due to exhaustion of some critical nutrient, or to accumulation of waste products that slow down growth (e.g.Note: useful to calculate doubling time can vary from 20 min to several days.Cells in optimum growth state, divide repeatedly by binary fission at maximal rate.Can reduce or eliminate lag phase by using cells that are not in stationary phase.Need to regenerate pools of essential nutrients before growth can resume, requires new enzyme synthesis and time for pathways to function. Previous cells ran out of food, shut down many metabolic pathways needed for active growth, made adaptations necessary for dormancy and protection.6.1 in text)Ĥ phases: lag, exponential, stationary, and death Prokaryotes grow by binary fission: 1 cell grows, divides into 2 identical daughters, etc.Good simulation for study of many natural environments. Trickle fresh medium into culture at slow but steady rate, displace = volume of culture as overflow.Ĭells remain in exponential (but suboptimal) state, growing at known rate. Common lab procedure, but not typical of many real environments. Batch method: put small inoculum of pure culture into sterile medium, let grow.
When should you inoculate? How can you know when you have reached the desired cell concentration? You need to grow bacteria to a concentration of 5 x 10 8 cells/ml, then harvest these cells for use in an experiment. You are hired as a research assistant in a laboratory. How will you decide? What numbers do you need? You must decide how much inoculum to put in tank, when to harvest bacteria for maximum profit, minimum cost. You have one 10,000 gallon tank available, costs $1000/day to run.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
